Kidney Disorders | kidney stones | Renal failure | Food to be used |
Kidney stones:
When the urine becomes too thick, many salts such as calcium oxalate, calcium and ammonium phosphate, uric acid, etc., become crystals. Crystals this large cannot pass through the urine and accumulate as solids. They are called kidney stones. Most kidney stones start in the kidneys. A few stones may also enter the ureter and bladder.
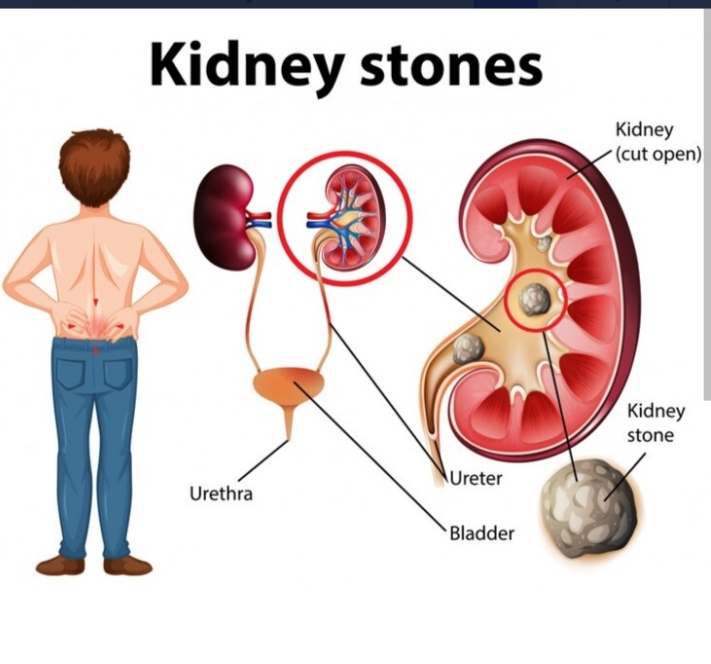
Causes:
The main causes of kidney stones are age, diet (high intake of green vegetables, salt, vitamin C and D), frequent urinary tract infections, low water intake and alcohol consumption.
Symptoms :
Symptoms of gallstones are:
🔹Severe kidney or lower abdominal pain,
🔹Frequent urination
🔹Diarrhea and foul-smelling urine containing blood and pus.
Treatment :
About 90% of stones can pass through the urinary system if you drink plenty of water. Surgical treatment involves opening the affected area and removing the stone from there. Another method of removing kidney stones is lithotripsy. In this method, the stones present in the urease system are removed from the outside. Electrical shock waves (non-electrical shock waves) are emitted. These rays hit large rocks and break them. Stones become like sand and are excreted in the urine.
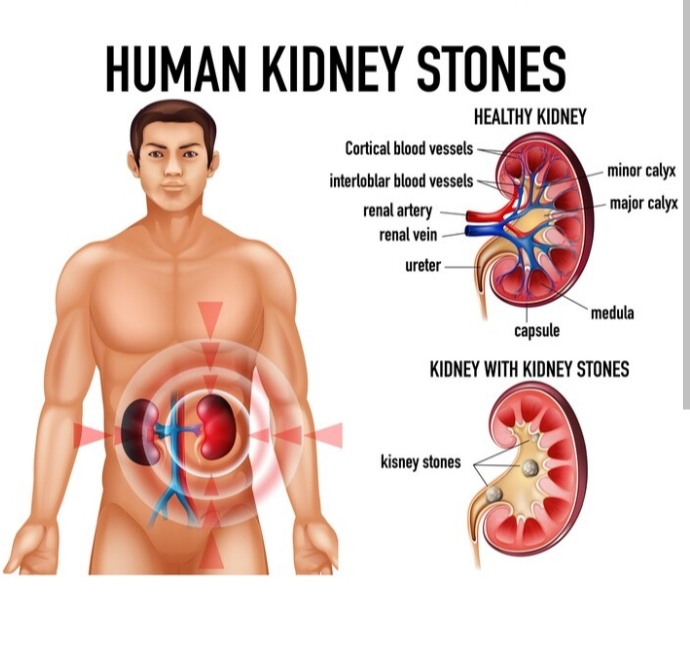
Kidney failure:
Complete or partial failure of kidney function is called kidney failure.
Causes:
Diabetes mellitus and hypertension are the main causes of kidney failure. Sometimes the blood supply to the kidneys is sudden Obstruction or too much medication can also cause kidney failure.
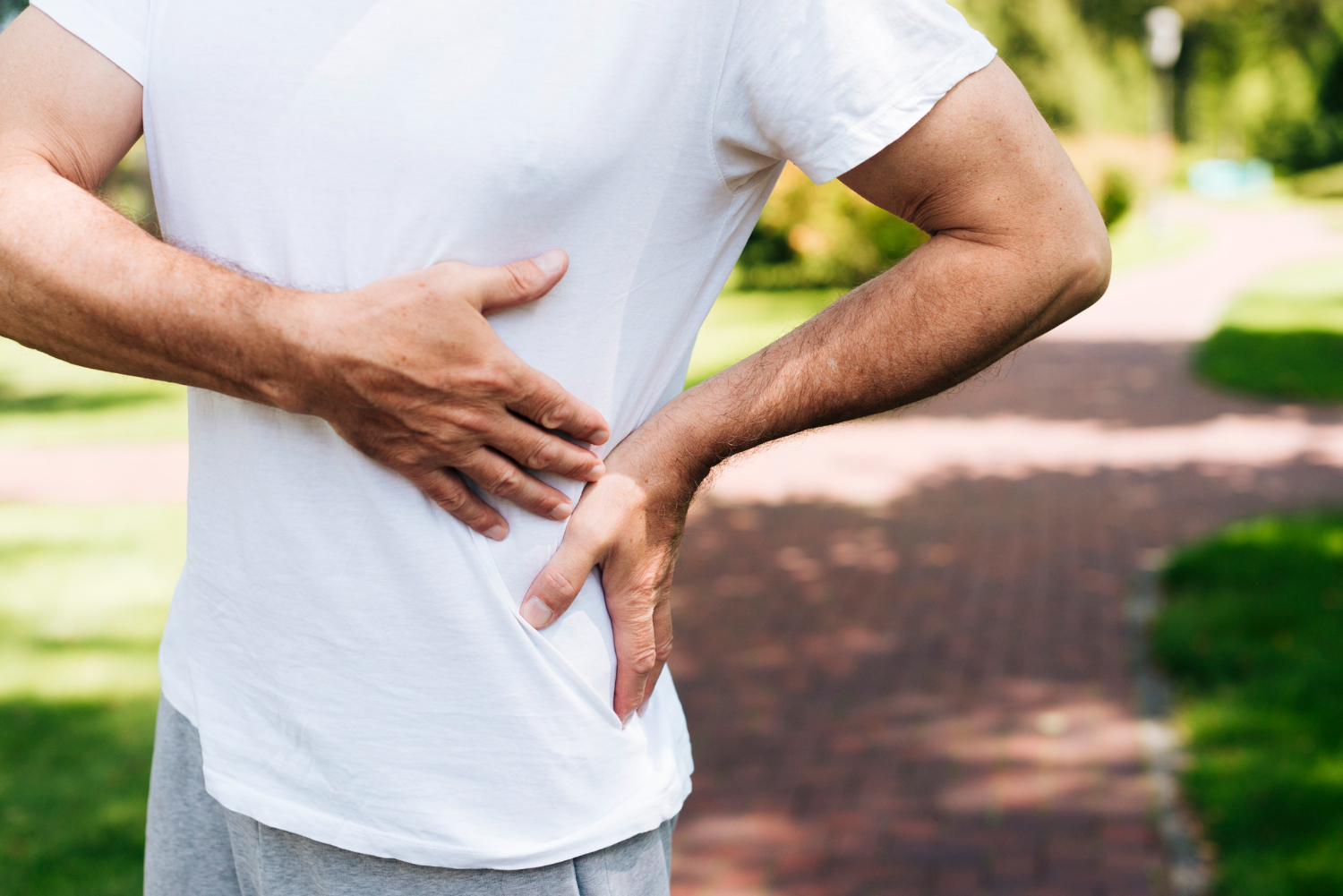

Symptoms :
Symptoms of kidney failure include increased levels of urea and other waste products in the blood, which can result in vomiting, nausea, weight loss, frequent urination, and blood in the urine. Excess fluid in the body can cause swelling of the legs, feet and face and shortness of breath. Treatment for kidney failure is dialysis and kidney transplantation is performed (kidney transplant)
Dialysis:
Dialysis refers to the purification of blood by artificial means. This is done in two ways.
1.Peritoneal dialysis: In this type of dialysis, the dialysis fluid is pumped into the peritoneum (digestive tube, i.e. the space around the intestine) for a set period of time. The walls of this cavity are lined with peritoneum, which contains blood vessels. When dialysis fluid is placed in the peritoneal cavity, abnormal substances present in the blood of the blood vessels of the peritoneum penetrate into the dialysis fluid. The dialysis fluids are then withdrawn. This type of dialysis can also be done at home, but must be done daily.
Hemodialysis:
In hemodialysis, the patient's blood is passed through a machine called a dialyzer. Inside the dialyzer are long valves whose walls act as semi-permeable membranes.
passes through the valves while the dialysis fluid flows around these valves.
Excess water and waste products leave the blood and enter the dialysis fluid. Cleaned blood is re-entered into the body. Hemodialysis is treated three times a week in dialysis centers.
Kidney transplant:
We know that dialysis needs to be repeated after a few days. This process is also unpleasant for patients and their companions. Another treatment for end-stage renal failure is a kidney transplant. In this treatment, the patient's failing kidney is replaced with a healthy kidney from a donor.
The donor can be living or dead. It is not mandatory for the kidney donor to be a relative of the patient. Before transplantation, the tissue proteins of the donor and the patient are tested for compatibility. The donor kidney is transplanted into the patient's body and connected to the circulatory and urinary systems.
The average lifespan of a donated kidney is 10 to 15 years. When the transplant fails, the patient can be transplanted with a new kidney. In such a case, the patient is treated with dialysis in the medium term. Post-transplant complications include tissue rejection, infection, and salt imbalances in the body (resulting in bone problems and complications). may be included).
Foods to be Used :
The appropriate dosage for patients with kidney stones and kidney failure depends on their condition and the severity of the disease. However, in general the following suggestions can be made:
For patients with kidney stones:
1.Water:
Drink plenty of water, about 8-10 glasses a day, to increase urine production and reduce the possibility of stone formation.
2.Fruits and Vegetables:
Eat more fruits and vegetables that can be beneficial for kidney health, such as cucumbers, watermelon and cantaloupe.
3.Low Sodium Diet:
Keep your salt intake low as excess salt can contribute to stone formation.
4.Calcium:
Consume balanced calcium as recommended by your doctor, avoid calcium supplements.
For patients with renal failure:
1.Limited water intake:
Water intake should be limited as directed by your doctor, as drinking too much water can be dangerous.
2.Low potassium intake:
Control potassium intake such as avoiding bananas, tomatoes and potatoes.
3.Lower Phosphorus Intake:
Keeping phosphorus intake low, such as avoiding milk and dairy products, sodas, and chocolate.
4.Limited protein intake:
Control your protein intake, especially limit meat, fish and eggs.
General tips:
1.BALANCED DIET:
Eat a balanced and healthy diet that contains essential vitamins and minerals.
2.Less intake of salt and sugar:
Keep your intake of salt and sugar low so that additional stress is not placed on the kidneys.
3.Consult your doctor:
It is important to consult your doctor or nutritionist before starting any new diet.
These suggestions are general in nature and each patient's condition is different, so it is important to consult a doctor for individual treatment and advice.
Recommended Blogs


Mansab Ali


Mansab Ali


Mansab Ali



